Cancer cell-selective clathrin-mediated endocytosis of aptamer-decorated nanoparticles
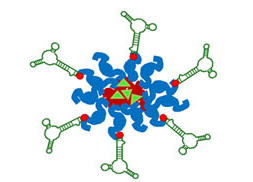
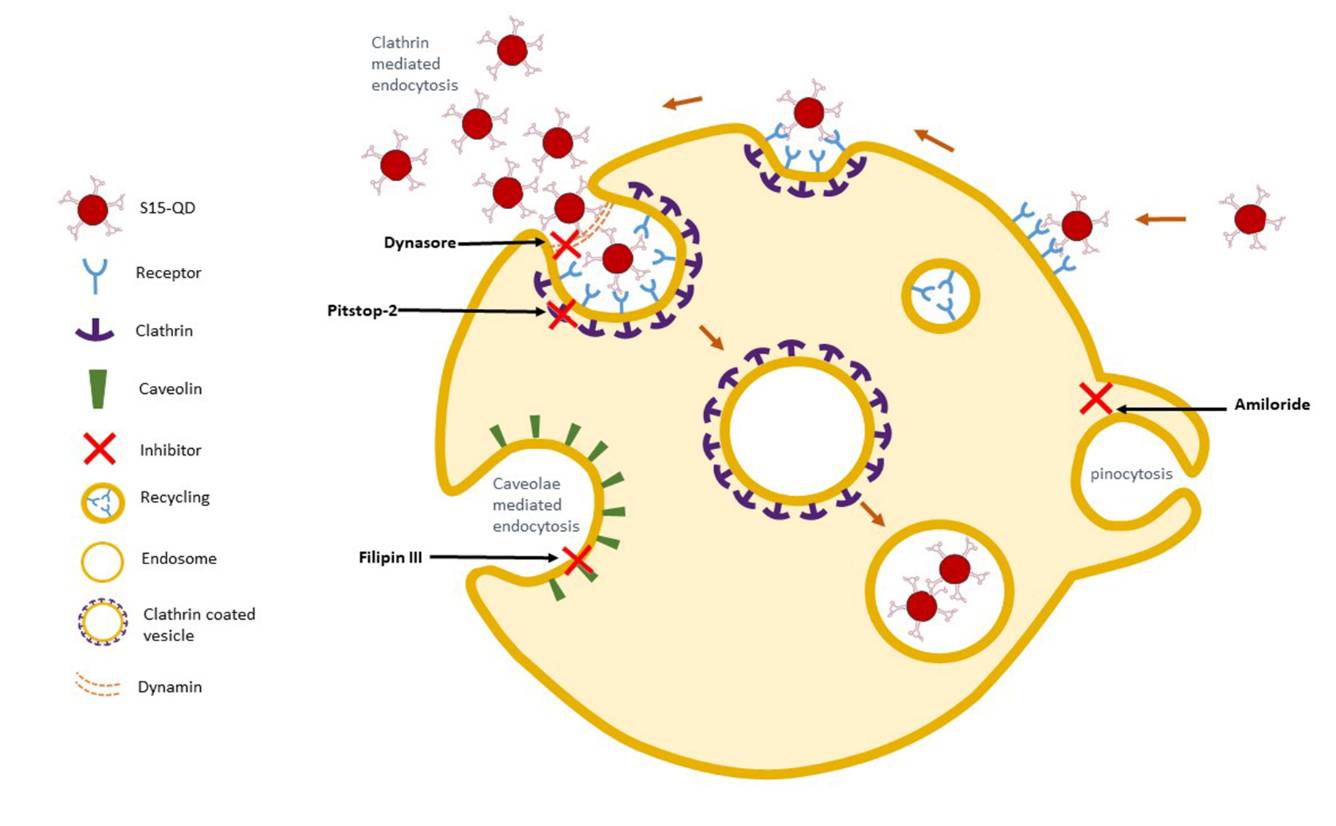
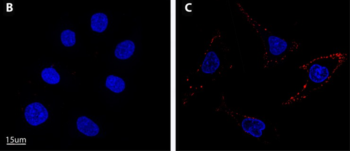
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide, resulting in 88% deaths of all diagnosed patients. Hence, novel therapeutic modalities are urgently needed. Single-stranded oligonucleotide-based aptamers (APTs) are excellent ligands for tumor cell targeting. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying their internalization into living cells have been poorly studied. Towards the application of APTs for active drug targeting to cancer cells, we studied the mechanism underlying S15-APT internalization into human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. We delineated the mode of entry of a model nanomedical system based on quantum dots (QDs) decorated with S15-APTs as a selective targeting moiety for uptake by A549 cells. These APT-decorated QDs displayed selective binding to, and internalization by target A549 cells, but not by normal human bronchial epithelial BEAS2B, cervical carcinoma (HeLa) and colon adenocarcinoma CaCo-2 cells, hence demonstrating high specificity. Flow cytometry analysis revealed a remarkably low dissociation constant of S15-APTs-decorated QDs to A549 cells (Kd = 13.1 ± 1.6 nM). Through the systematic application of a series of established inhibitors of known mechanisms of endocytosis, we showed that the uptake of S15-APTs proceeds via a classical clathrin-dependent receptor-mediated endocytosis. This cancer cell-selective mode of entry could possibly be used in the future to evade plasma membrane-localized multidrug resistance efflux pumps, thereby overcoming an important mechanism of cancer multidrug resistance.
Selective eradication of human non-small cell lung cancer cells using aptamer-decorated nanoparticles harboring a cytotoxic drug cargo
Targeted cancer therapy is currently the leading modality to enhance treatment selectivity and efficacy, as well as to minimize untoward toxicity to healthy tissues. Herein, we devised and studied nanoparticles (NPs) composed of the biocompatible block-copolymer PEG-PCL entrapping the hydrophobic chemotherapeutic drug paclitaxel (PTX), which are targeted to human non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells. To achieve selective NSCLC targeting, these NPs were decorated with single-stranded oligonucleotide-based S15 aptamers (S15-APTs), which we have recently shown to serve as efficient tumor cell targeting ligands. Prepared without using surfactants, these 15 nm PEG-PCL/PTX NPs entered NSCLC cells via clathrin-mediated endocytosis. These NPs demonstrated efficient encapsulation of PTX, high selectivity to- and potent eradication of human A549 NSCLC cells, with a remarkable half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of 0.03 μM PTX. In contrast, very high IC50 values of 1.7, 4.2, 43, 87, and 980 μM PTX were obtained towards normal human bronchial epithelial BEAS2B, cervical carcinoma HeLa, colon adenocarcinoma CaCo-2, neonatal foreskin fibroblast FSE, and human embryonic kidney HEK-293 cells, respectively. These results demonstrate 2–5 orders
of magnitude difference in the selective cytotoxicity towards NSCLCs, reflecting a potentially outstanding therapeutic window. Moreover, the dual utility of aptamer-decorated NPs for both drug stabilization and selective tumor targeting was studied by increasing APT concentrations during NP “decoration”. The optimal aptamer density on the surface of NPs for selective targeting, for high fluorescence diagnostic signal and for maintaining small particle size to enable endocytosis, was achieved by using 30 nM APTs during NP decoration. Collectively, our findings suggest that these APT-decorated NPs hold great preclinical promise in selective targeting and eradication of human NSCLC cells without harming normal tissues.

Research
Biomed
Aptamer-based selective targeting of chemotherapeutics-loaded NPs
Relevant publications:
Cancer cell-selective clathrin-mediated endocytosis of aptamer-decorated nanoparticles
Oncotarget, 9(30), 20993-21006, (2018)
Selective eradication of human non-small cell lung cancer cells using aptamer-decorated nanoparticles harboring a cytotoxic drug cargo
Cell death & disease, 10(10), 1-14,(2019).